Hemocytometer: The Gold Standard for Cell Counting
Precision matters in the lab. Whether you're counting red blood cells, white blood cells, or bacteria, a hemocytometer also known as a cell counting chamber is your ultimate ally. Despite the rise of automated systems, hemocytometers remain indispensable, especially for smaller labs or specialized applications. Let’s dive into why this tool is essential, how to use it effectively, and how it stacks up against alternatives.
What Is a Hemocytometer?
A hemocytometer is more than just a slide; it’s a masterpiece of precision engineering. It’s a specialized glass slide with a grid etched into its surface, designed to count cells in a liquid sample. The chamber’s uniform depth (usually 0.1 mm) and the engraved grid allow for accurate cell counting when used with a microscope.
But it’s not just about counting it's about reliability. By analyzing a small sample, you can calculate cell concentrations with ease.
Why Are Hemocytometers Still a Lab Staple?
In an era of high-tech gadgets, you might wonder why hemocytometers are still widely used. Here’s why:
- Cost-Effective: Automated cell counters are expensive. For smaller labs, a hemocytometer is an affordable alternative.
- Flexibility: Whether it’s cerebrospinal fluid, bacteria, or even fungal spores, hemocytometers handle it all.
- Precision for Low Counts: In samples with fewer cells like cerebrospinal fluid a hemocytometer outperforms many automated systems.
The Grid That Makes It All Possible


The most commonly used hemocytometer is the Improved Neubauer grid, and for good reason. Its design allows for versatility:
- Central Square: Perfect for counting platelets and red blood cells.
- Corner Squares: Ideal for white blood cells.
- Subdivisions: Each square is divided into smaller units, making it easy to count even the tiniest particles.
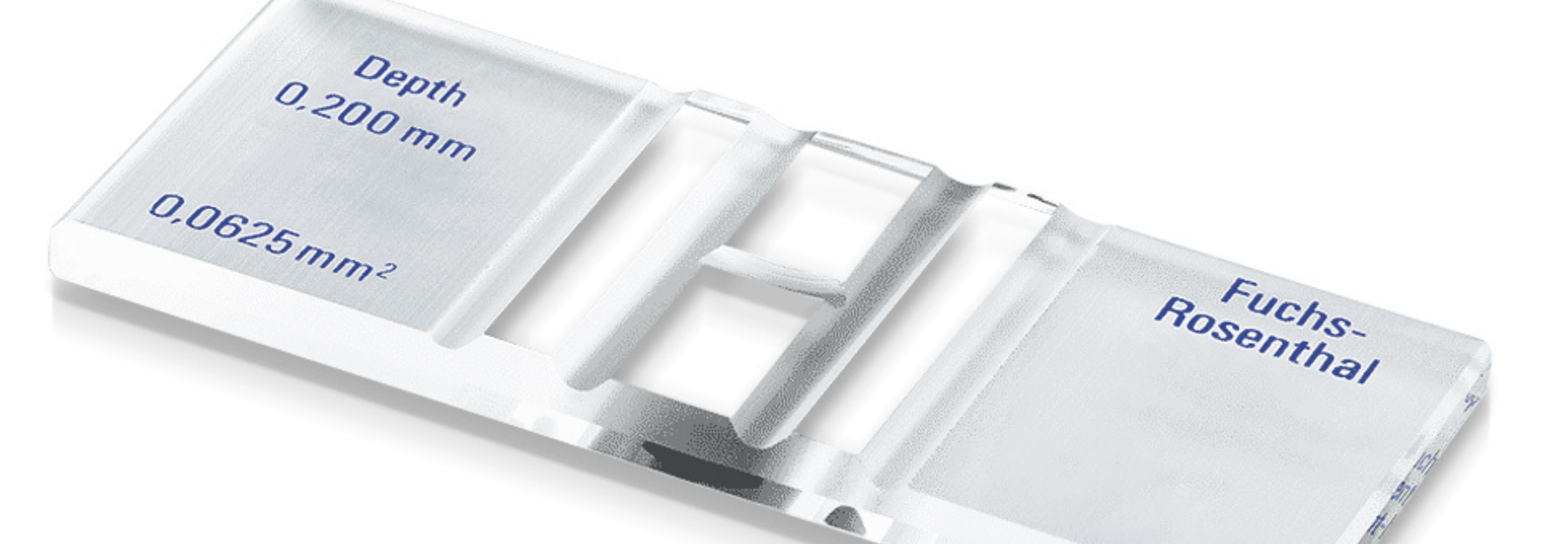
Other grids, like the Bürker-Türk or Fuchs-Rosenthal, cater to specific needs. For example, the Fuchs-Rosenthal grid is often used for cerebrospinal fluid, thanks to its larger depth (0.2 mm) and volume capacity.
How to Use a Hemocytometer: Step-by-Step
- Prepare Your Sample: Ensure your suspension is well-mixed to avoid clumping or uneven distribution.
- Load the Chamber: Use a pipette to fill the chamber with your sample. Be cautious avoid overfilling!
- Place the Cover Glass: The chamber and cover glass together define the precise volume of the sample.
- Count Under the Microscope: Focus on the grid and count cells within the appropriate squares.
- Calculate Concentration: Use the formula:

Pro Tips for Accurate Results
- Avoid Overloading: Too much sample can obscure the grid, leading to inaccurate counts.
- Focus Matters: Adjust your microscope carefully to see the grid lines clearly.
- Repeat Counts: Perform at least two counts and average them to improve accuracy.
Which Hemocytometer Is Right for You?
The type of hemocytometer you need depends on your application:
- Improved Neubauer: The go-to for most labs.
- Fuchs-Rosenthal: Ideal for cerebrospinal fluid.
- Malassez: A classic choice for specific applications.
Each grid has unique features that cater to various sample types and concentrations.
Why Smartlabs Is Your Hemocytometer Destination
At Smartlabs, we offer a curated selection of hemocytometers, including the popular Improved Neubauer grid. Whether you’re in education, research, or professional practice, our tools are designed for precision and reliability.
Final Thoughts
The hemocytometer isn’t just a tool it’s a cornerstone of laboratory science. With its unmatched accuracy and versatility, it continues to empower scientists worldwide. Whether you’re counting blood cells, analyzing cerebrospinal fluid, or studying bacterial cultures, the hemocytometer remains an essential instrument.
Explore our range of hemocytometers today and elevate your lab’s precision!
